What it was never told about the receipt of electricity
The Spanish electricity system
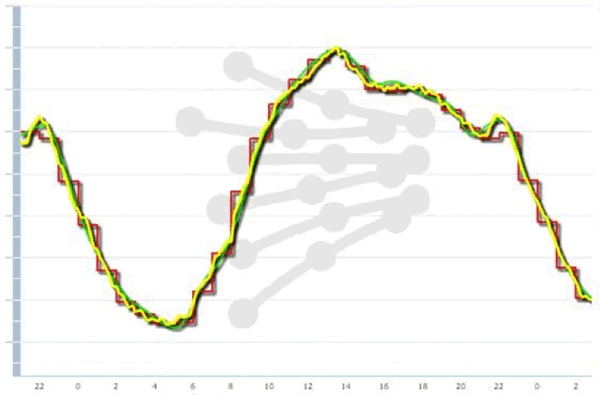
The Spanish electricity system, like any electrical system, is complex because nobody escapes us that electricity demand is variable. Our electricity consumption varies throughout the day, throughout the week and depending on the season … It even depends on whether it is raining or the sun, if it’s cold or heat, and thousands of random components, such as if we want the washer today or tomorrow.
It is therefore a complex system from a technical point of view, because it consumed at every moment being produced at that moment.
 The Spanish power system is divided into different actors of the system:
The Spanish power system is divided into different actors of the system:
Generation: responsible for generating electricity from a given resource. For example nuclear plants or wind generators.
Transportation: REE (Red Electrica Española) is responsible, for transporting the energy produced by the generation over long distances that are saved by using power lines. It must be transported at high voltage so that losses results the lowest possible.
Distribution: bringing electricity to consumers through lines of medium and low voltage. It is the whole network of wiring and electrical substations that make electricity reaches our homes. The distribution depends on the distribution utilities in each area: Iberdrola, Endesa …
Consumption: formed by all energy consumers.
 Brief history of liberalization Electric System
Brief history of liberalization Electric System
Before 1997 … the electrical system was governed by the Legal Framework Stable, wherein the electrical activity was regulated, giving back the state each company an adequate return so they could carry out their activities within the system.
From 1997 to 2009 … a progressive liberalization of the electricity market is made up of what today is known as the Iberian electricity market. State management remains in the transportation and maintenance of networks and the generation and marketing are liberalized. A retail and wholesale market is established. The traders come to the wholesale market and then sell electricity at retail to residential consumers and small businesses.
Currently … The price of kWh encompasses a portion to cover the costs of the system (the regulated portion covering the maintenance of lines, premiums for renewable and cogeneration, payment of nuclear moratorium island offsets system, etc.) and the part of the free market from the purchase of electricity in the electricity market. The state receives from the regulated party marketers and divides between actors transmission and distribution to cover its costs recognized.
 A brief history of the pricing of electricity
A brief history of the pricing of electricity
Until July 1, 2009 … there was the full fare, with which the state set the price of electricity each year, including both regulated components as the free market.
July 1, 2009 … go the old rates and all consumers had to go to the retail market, contracting with a marketer. For that to July 1, 2009 it had not done (almost 90% of consumers) a fee is designed, called Last Resort Rate (TUR) which is automatically passed. The price of electricity for the TUR consisted of:
- Component regulated, set by the state, which was used to cover the costs of the system.
- Component free market, fixed by the CESUR (electricity auction conducted quarterly).
The price of TUR was obtained by adding to the auction CESUR regulated component and a profit margin stipulated by the administration to suppliers of last resort.
For consumers attached to the TUR (Last option Tariff), the price was set every three months by auction (CESUR). At the auction, the price will be added to the regulated component and the profit margin allocated to suppliers of last resort and posted on the BOE the price of electricity every 3 months.
The CESUR auction system for pricing consisted of an auction of electricity organized by OMEL (the electricity market operator) quarterly. Involved large utilities, banks and investment funds that were pushing for electricity that was consumed in the coming months, so that undertook to buy the electricity were to sell in the daily auction and pay generators as daily price appeal (is the price reaches electricity for each hour, where supply and demand match). However, the electricity sold to traders at a fixed price, which undertook to sell electricity at the lowest price was wearing the auction.
The risk assumed winners CESUR auction was obliged to buy at the price out daily (called pool) and sell at a fixed price each quarter
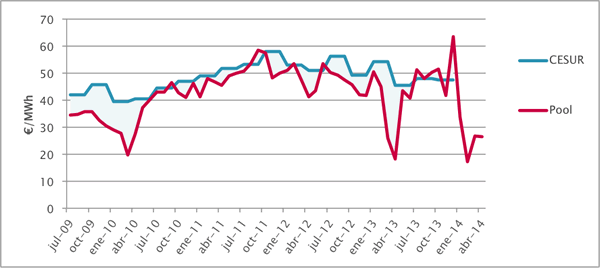
In general, except rarely the final price at which they bought was less than it had agreed to sell, which entailed a major profit for the participating companies of this auction, and of course an extra cost to the electrical system for the sake of having priced to periods of three months.
The outcome of the twenty-fifth auction held in December 2013 is void in the resolution of December 20, 2013 by the Secretary of State for Energy. The result of the auction was a high price involving an unaffordable price for the following quarter. Which showed that the system had its shortcomings and concurrently certain circumstances could pose an enrichment of some at the expense of all consumers.
As of April 1, 2014 … is instituted a new model to replace the bearing in operation since 2009. The pricing by the CESUR auction mechanism disappears. The energy term, fixed for 3 months before by this mechanism, now every day is established as a result of the wholesale market and is different for each of the 24-hour price. Is PVPC (Voluntary Price for the Small Consumer).
July 1, 2014 becomes a mandatory system, having to settle sums paid more in the first half of 2014. If you have a digital meter with remote management shall apply the appropriate time reading, if not apply average consumption preset profiles.
Alternatively, consumers can opt for a fixed annual fee that marketers reference (before the last option retailers) must offer.
Today all year fixed rates have been more expensive than PVPC. While not the best system is generally cheaper for small consumers of electricity that offers marketers.

Pol Parareda Farriol es ingeniero industrial y MBA, con más de 15 años de experiencia internacional en el sector de la energía solar fotovoltaica y las energías renovables. Actualmente Director en Tienda Solar, trabaja en el desarrollo y gestión de soluciones de autoconsumo, sistemas fotovoltaicos y almacenamiento con baterías para el mercado residencial y profesional.
A lo largo de su carrera ha ocupado puestos de responsabilidad en empresas líderes del sector como Weidmüller, SunPower, Sunco Capital y Hilti, desempeñando funciones en ingeniería, desarrollo de producto, operaciones, O&M, gestión comercial y dirección estratégica de proyectos solares, tanto a pequeña escala como en grandes plantas fotovoltaicas internacionales.
Ha liderado proyectos y equipos en Europa, Latinoamérica y Asia, participando en el desarrollo de más de cientos de MW en proyectos solares, negociación de PPAs, estrategias EPC y optimización de sistemas fotovoltaicos. Además, ha sido docente de energía solar fotovoltaica en programas de máster en energías renovables en instituciones como la Universidad Carlos III de Madrid





